In this pfSense DNS Server Guide, I want to give you an introduction into the world of DNS. What is DNS and what does it do inside of your pfSense box?
As you know these tutorials are more guided towards beginners, so I won’t go too deep into the material.
DNS translates to Dynamic Name System. Every homepage on the internet is actually an IP Address. So, for example, if you want to go over to Google to search something you type www.google.com, which actually isn’t the address of Google.
The real address of Google looks more like this: 172.217.22.100. So what does DNS do? It sends your request of reaching www.google.com to a DNS server that has all those IP Addresses stored and translates it into an IP address and finally sends you to your destination.
That is a brief introduction, the topic is very complex but if you get this basic understanding of it down, you are good enough to go.
There are 2 options in pfSense for DNS:
- DNS Forwarder
- DNS Resolver
In this guide we will only focus on the DNS resolver, which makes your pfSense firewall a DNS server for your internal network, translating internal device’s IP addresses to hostnames in its internal database such as:
my desktop computer = 192.168.1.25
A DNS Forwarder would forward that request to another DNS Server with recursive capabilities (like a caching DNS Server). But as I said, we will not go deeper into this to avoid confusion for now. A good example would be if you run a domain controller inside of your network that handles DNS, so you would forward all DNS requests to your domain controller.
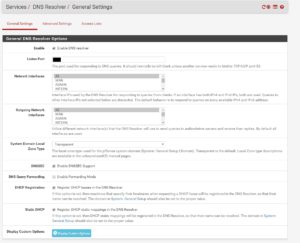
So let’s log into our pfSense and go to Services -> DNS Resolver
The DNS Resolver is enabled by default in your pfSense installation. You should see something like this:
We can leave everything on default here. Just make sure it’s enabled.
Next, we go to System -> General Setup
For you, those 4 DNS Server lines will be empty and for the beginning that’s perfectly fine. Normally you will get a DNS server assigned over your WAN interface directly from your Internet Service Provider. So for a real basic setup, you don’t need to bother with DNS anymore.
You probably ask yourself why I have a few servers there? Well, there are certainly (but not always) better and faster servers available out there. It also depends on how far the server of your ISP is from your location and how good it is.
There is a tool for that, I made a short video of how to improve your surf speed by optimizing your DNS servers here.
There will be a separate in-depth and step by step written tutorial about this later on.
So yeah guys, that’s really it with basic DNS what you need to know to run your pfSense firewall. Just make sure you use DNS Resolver and all the standard settings should run fine for you.
There will be a more detailed article and video about DNS in the pfSense Advanced Tutorial Series I will release after this basic series.
As always, hope you enjoyed reading and I could clarify a thing or two. Go ahead and throw any questions at me below in the comments.
- Firewall Micro Appliance With 4x Gbe Intel Lan Ports for PFSense
- Firewall Micro Appliance with 2x Gbe Intel LAN Ports for PFSense Barebone
- Firewall micro appliance with 4x Gigabit Intel LAN Ports for pfSense with 4GB RAM / 16GB mSATA
- Firewall micro appliance with 2x Gigabit Intel LAN Ports for pfSense with 2GB RAM / 16GB mSATA



Sorry, but DNS stands for “Domain Name System”, nothing’s dynamic there. Accept you use DynDNS…
I have a problem I made a dns resolver on the pfsence so that the user who is in LAN can access the web server which in WAN with a domain name for example http://www.web.com but it doesn’t work I know not what the problem is, (user can access the web server without any problem with the ip address because I configured the NAT so that the internal user’s address translates into a public address by pfsense) can you help me to know what the problem is, did I not configure the DNS resolver correctly? and thank you